Securing the Future of Industrial IoT: GRC and VAPT Strategies for Industry 4.0
As we move deeper into the era of Industry 4.0, the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) has transformed manufacturing, logistics, and other critical industries by enabling smarter, more connected systems. However, this increased connectivity introduces a range of new cybersecurity challenges, with attacks on Industrial IoT (IIoT) devices becoming more sophisticated and disruptive. To protect these systems, a combination of Governance, Risk, and Compliance (GRC)frameworks and Vulnerability Assessment and Penetration Testing (VAPT) strategies is essential
In this blog, we will explore what cyber hygiene entails, its impact on cyber insurance, and why organizations should prioritize it.
The Rise of Industrial IoT in Industry 4.0
The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) refers to the network of interconnected devices and sensors used in industrial operations, from manufacturing floors to power grids. These smart devices generate and share massive amounts of data, improving efficiency, reducing operational costs, and enabling real-time decision-making.
Key applications of IIoT in Industry 4.0 include:
- Smart manufacturing: Automated machines and robots connected to a central system for seamless production and efficiency.
- Predictive maintenance: Sensors monitor equipment health and predict failures before they happen.
- Supply chain optimization: Real-time monitoring of goods in transit to ensure timely delivery and optimize logistics.
- Energy management: Monitoring and controlling energy consumption across industrial facilities for cost savings and sustainability.
However, the same connectivity that makes these systems smart also introduces significant security risks. The reliance on a network of IIoT devices creates a large attack surface that cybercriminals can exploit, putting critical infrastructure and sensitive industrial data at risk.
Understanding the Security Challenges in Industrial IoT
IIoT environments are often complex and integrate both legacy systems and new technologies. This mix creates several cybersecurity challenges unique to industrial settings:
- Increased Attack Surface: With multiple devices, sensors, and systems connected over the internet, IIoT environments become more vulnerable to attacks. Each device represents a potential entry point for hackers.
- Outdated Systems: Many industrial operations still use legacy systems that lack modern security features. These systems are often hard to patch or upgrade, leaving them vulnerable to cyberattacks.
- Critical Infrastructure at Risk: Disruptions in IIoT environments can have far-reaching consequences. Attacks targeting manufacturing plants, energy grids, or transportation systems can cause widespread operational and economic damage.
- ⦁ Lack of Standardization: Unlike IT systems, the security standards for IIoT are still evolving. This lack of standardization makes it difficult to ensure consistent security measures across different devices and vendors.
To address these challenges, organizations need to adopt a robust security strategy combining GRC frameworks and VAPT methodologies to safeguard IIoT environments.
Governance, Risk, and Compliance (GRC) in Industrial IoT Security
Governance, Risk, and Compliance (GRC) is a holistic approach to managing an organization’s overall security posture. GRC frameworks provide the structure and processes necessary to manage risk, ensure compliance with regulatory requirements, and establish a secure operational environment. When applied to IIoT, GRC plays a crucial role in mitigating risks while maintaining operational efficiency.
-
Governance
-
Risk Management
-
Compliance
In the context of IIoT, governance involves setting clear security policies and procedures to manage how data and systems are protected. It includes defining roles and responsibilities, establishing security baselines, and ensuring that all stakeholders follow established guidelines. Proper governance ensures that cybersecurity efforts are aligned with broader organizational goals.
Effective risk management is essential for identifying and mitigating security risks in IIoT environments. This includes conducting regular risk assessments to evaluate potential threats, identifying vulnerabilities in connected devices, and determining the potential impact of a breach. By understanding the risks, organizations can prioritize their security investments and make informed decisions.
Industrial sectors often have to comply with stringent regulatory requirements, such as the NIST Cybersecurity Framework, ISO 27001, and industry-specific regulations. Compliance ensures that IIoT systems meet legal and regulatory standards. GRC frameworks help organizations stay compliant by incorporating regular audits, reporting mechanisms, and security assessments into their operations.
By implementing a strong GRC framework, organizations can establish a secure foundation for their IIoT operations, minimize risks, and ensure they meet industry standards and regulations.
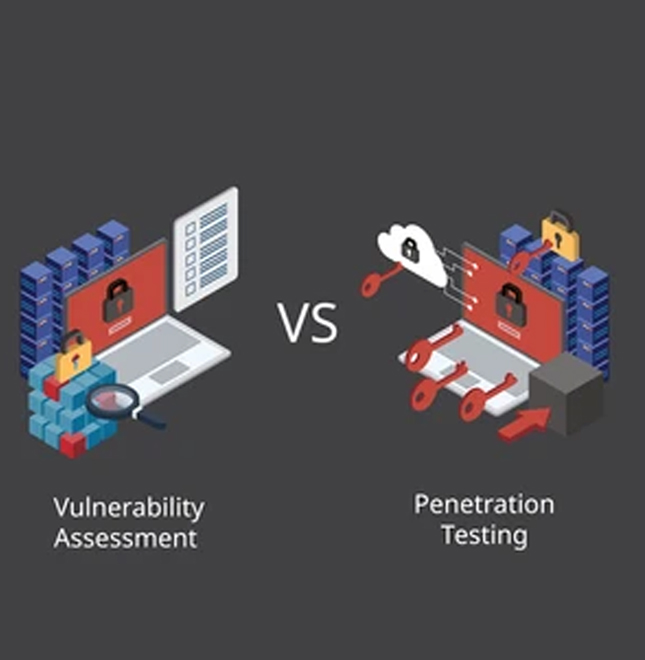
The Role of VAPT in Securing Industrial IoT
While GRC provides the structure to manage security and compliance, Vulnerability Assessment and Penetration Testing (VAPT) offers the tools to actively identify and address vulnerabilities within IIoT systems. VAPT is a proactive approach to discovering weaknesses before cybercriminals exploit them.
- Vulnerability Assessment
- Device and Network Scanning: Identifying unpatched vulnerabilities, weak encryption, and insecure communication protocols.
- Configuration Reviews: Ensuring that IIoT devices are configured according to security best practices and not exposing sensitive data.
- Patch Management: Keeping all devices updated with the latest security patches to mitigate risks from known vulnerabilities.
-
Penetration Testing
Penetration testing goes beyond vulnerability scanning by simulating real-world attacks on IIoT systems. Ethical hackers (or penetration testers) use the same tactics as cybercriminals to exploit vulnerabilities and assess the effectiveness of an organization’s security measures. Penetration testing for IIoT devices provides critical insights into how well these systems can withstand cyberattacks and identifies gaps that need to be addressed. - Network and Device Exploitation : Testing for weak points in device firmware, communication protocols, and network configurations that can be exploited.
- Denial-of-Service (DoS) Attacks: Simulating attacks that could disrupt IIoT devices and shut down industrial operations.
- Physical Security: Assessing whether physical access to IIoT devices, such as sensors on a manufacturing floor, could be exploited to cause damage.
A vulnerability assessment involves scanning IIoT systems and devices for known security flaws, misconfigurations, or outdated software. This process helps organizations understand where their weaknesses lie and which systems require immediate attention. Regular vulnerability assessments are essential to maintain a strong security posture in constantly evolving IIoT environments.
Key components of a vulnerability assessment for IIoT systems include:
Key aspects of penetration testing in IIoT environments include:
By combining regular vulnerability assessments with in-depth penetration testing, organizations can identify weaknesses and improve the resilience of their IIoT infrastructure.
Best Practices for Securing Industrial IoT with GRC and VAPT
To effectively secure IIoT systems, organizations should integrate GRC frameworks with regular VAPT activities. Here are a few best practices to follow:
- Establish a Comprehensive GRC Framework: Define security policies, procedures, and roles that cover the entire IIoT ecosystem, from device management to data privacy.
- Conduct Regular Risk Assessments: Perform periodic risk assessments to identify evolving threats in the IIoT landscape and prioritize security investments accordingly.
- Perform Vulnerability Assessments and Penetration Tests: Regularly scan IIoT devices and systems for vulnerabilities and conduct penetration tests to validate the effectiveness of your security controls.
- Patch Management and Updates: Implement a robust patch management process to ensure all IIoT devices are running the latest security updates, and legacy systems are hardened against known vulnerabilities.
- Compliance Audits: Regularly audit IIoT systems to ensure they meet regulatory and industry compliance standards.
- Incident Response Planning: Develop and test incident response plans specific to IIoT environments to ensure quick recovery in the event of a cyberattack.
Conclusion
As the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) becomes more prevalent in Industry 4.0, securing these connected systems is essential to ensuring the safety, efficiency, and resilience of critical operations. A combination of GRC frameworks and VAPT methodologies provides a robust approach to protecting IIoT environments from cyber threats.
By implementing strong governance practices, managing risks, ensuring compliance, and proactively identifying vulnerabilities through VAPT, organizations can safeguard their IIoT infrastructure, minimize risks, and drive innovation securely in the era of Industry 4.0.
At Risknox, we specialize in helping industrial organizations secure their IIoT systems through a combination of advanced GRC solutions and VAPT services. Contact us to learn how we can help you protect your IIoT assets and future-proof your operations against emerging cyber threats.
Lets Get Stared with Us.
Call Us Now!